Update Data in a Graph Network: Cypher MERGE
Graph Networks are Mutable
The code cited in this post comes from kuzu_merge.rs. To run that however, you’ll need to execute kuzu_create_return.rs first in order to provision a graph database and populate it with with data. kuzu_create_return.rs need only be executed once. Both Rust programs work with the graph database created in /tmp/kuzu_db.
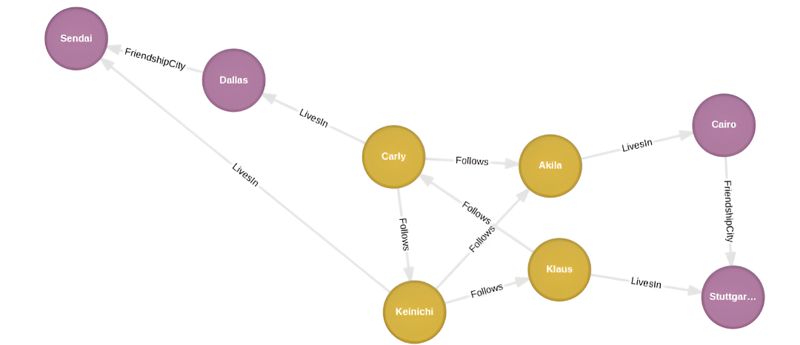
With the graph network we put together in earlier post, we have users that follow one another in a unidirectional way. Let’s say we want to update the database such that not only does Carly follow Akila, but Akila too in reverse. Similarly we see that Akila and Klaus do not follow one another; let’s say we also want them to share a Follows relationship – say Klaus follows Akila. We accomplish this in Cypher using the MERGE clause.
MATCH and then MERGE
In the Cypher language MERGE is the way by which we apply updates to the graph database. To use this clause, we must first supply it with patterns that are anchored by Cypher reference variables. We do so by means of the MATCH clause.For example, here’s how we create a relationship between two existing nodes:
MATCH (u1: User {name: 'Klaus'})
MATCH (u2: User {name: 'Akila'})
MERGE (u1)-[:Follows {since: DATE('2024-01-25')}]->(u2)
MERGE (u2)-[:Follows {since: DATE('2024-01-25')}]->(u1)
RETURN u1, u2Here our pattern matches the reference variables u1 and u2 with the nodes for Klaus and Akila. With this in hand we then create a pair of Follows relationships and store the new information to the graph database.
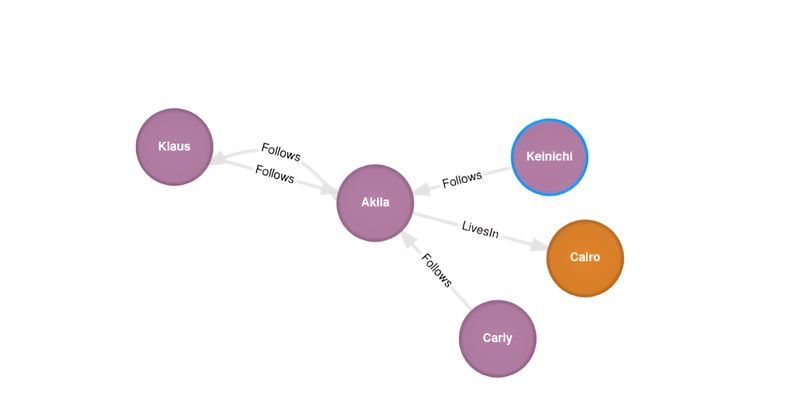
Knowing all this, it becomes trivial to insert a new User node into the graph network and create new Follows relationships for it.
MATCH (c: City {name: 'Dallas'})
MATCH (u1: User {name: 'Carly'})
MERGE (u2: User {name: 'Tom', age: 22})
MERGE (u2)-[: LivesIn]->(c)
MERGE (u2)-[: Follows]->(u1)
MERGE (u1)-[: Follows]->(u2)
RETURN u1, u2, c 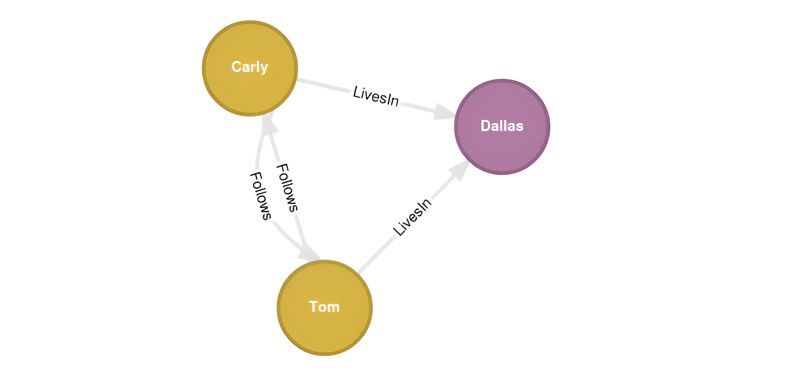
Note that Cypher requires all MATCH patterns to come before MERGE clauses; changing the order leads to an error.